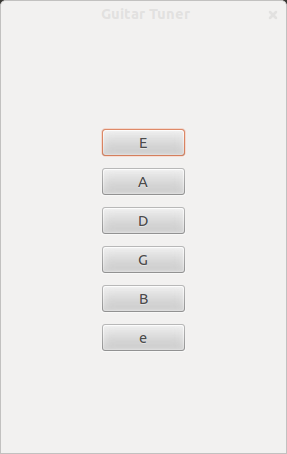
Creating the main window for the application
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Gtk.init(null, 0);
Gst.init(null, 0);
var guitarwindow = new Gtk.Window({type: Gtk.WindowType.TOPLEVEL, border_width: 100});
guitarwindow.title = "Guitar Tuner";
guitarwindow.connect("destroy", function(){Gtk.main_quit()});
guitarwindow.show();
Gtk.main();
Importing Gtk and Gst is not enough, we need to initialize them in order to get them working. When Gtk and Gst are up and running we need to create the window for the application. Later we are going to put all the buttons for making sounds inside this window. In order to get the window showing, we need to tell it to show and we need also to run the code with the Gtk.main()