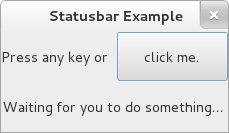
This statusbar tells you what's going on.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62
public class MyWindow : Gtk.ApplicationWindow {
Gtk.Statusbar statusbar;
uint context_id;
internal MyWindow (MyApplication app) {
Object (application: app, title: "Statusbar Example");
statusbar = new Gtk.Statusbar ();
context_id = statusbar.get_context_id ("example");
statusbar.push (context_id, "Waiting for you to do something...");
//set the default size of the window
this.set_default_size (200, 100);
var grid = new Gtk.Grid ();
var label = new Gtk.Label ("Press any key or ");
grid.attach (label, 0, 0, 1, 1);
label.show ();
var button = new Gtk.Button.with_label ("click me.");
grid.attach_next_to (button, label, Gtk.PositionType.RIGHT, 1, 1);
button.show ();
grid.attach (statusbar, 0, 1, 2, 1);
statusbar.show ();
grid.set_column_spacing (5);
grid.set_column_homogeneous (true);
grid.set_row_homogeneous (true);
this.add (grid);
grid.show ();
button.clicked.connect(button_clicked_cb);
}
/* Since the key-press-event is a signal received by the window, we don't need to connect
the window to a callback function. We can just override key_press_event. */
protected override bool key_press_event (Gdk.EventKey event) {
statusbar.push (context_id, Gdk.keyval_name(event.keyval) + " key was pressed.");
return true;
}
void button_clicked_cb (Gtk.Button button) {
statusbar.push (context_id, "You clicked the button.");
}
}
public class MyApplication : Gtk.Application {
protected override void activate () {
new MyWindow (this).show ();
}
internal MyApplication () {
Object (application_id: "org.example.status");
}
}
public int main (string[] args) {
return new MyApplication ().run (args);
}
In this sample we used the following:
Got a comment? Spotted an error? Found the instructions unclear? Send feedback about this page.