| Top |
Functions
Types and Values
| CoglObject | |
| CoglUserDataKey | |
| #define | COGL_INVALID_HANDLE |
| typedef | CoglHandle |
| enum | CoglPixelFormat |
| enum | CoglBufferTarget |
| enum | CoglBufferBit |
| enum | CoglAttributeType |
| enum | CoglFeatureFlags |
| enum | CoglFogMode |
| enum | CoglReadPixelsFlags |
Functions
cogl_object_ref ()
void *
cogl_object_ref (void *object);
Increases the reference count of object
by 1
[skip]
cogl_object_unref ()
void
cogl_object_unref (void *object);
Drecreases the reference count of object
by 1; if the reference
count reaches 0, the resources allocated by object
will be freed
[skip]
cogl_object_get_user_data ()
void * cogl_object_get_user_data (CoglObject *object,CoglUserDataKey *key);
Finds the user data previously associated with object
using
the given key
. If no user data has been associated with object
for the given key
this function returns NULL.
[skip]
Parameters
object |
The object with associated private data to query |
|
key |
The address of a CoglUserDataKey which provides a unique value with which to index the private data. |
Returns
The user data previously associated
with object
using the given key
; or NULL if no associated
data is found.
[transfer none]
Since: 1.4
cogl_object_set_user_data ()
void cogl_object_set_user_data (CoglObject *object,CoglUserDataKey *key,void *user_data,CoglUserDataDestroyCallback destroy);
Associates some private user_data
with a given CoglObject. To
later remove the association call cogl_object_set_user_data() with
the same key
but NULL for the user_data
.
[skip]
Parameters
object |
The object to associate private data with |
|
key |
The address of a CoglUserDataKey which provides a unique value with which to index the private data. |
|
user_data |
The data to associate with the given object,
or |
|
destroy |
A CoglUserDataDestroyCallback to call if the object is
destroyed or if the association is removed by later setting
|
Since: 1.4
cogl_handle_ref ()
CoglHandle
cogl_handle_ref (CoglHandle handle);
Increases the reference count of handle
by 1
cogl_handle_unref ()
void
cogl_handle_unref (CoglHandle handle);
Drecreases the reference count of handle
by 1; if the reference
count reaches 0, the resources allocated by handle
will be freed
CoglFuncPtr ()
void
(*CoglFuncPtr) (void);
The type used by cogl for function pointers, note that this type is used as a generic catch-all cast for function pointers and the actual arguments and return type may be different.
cogl_get_features ()
CoglFeatureFlags
cogl_get_features (void);
cogl_get_features has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_foreach_feature() instead
Returns all of the features supported by COGL.
Since: 0.8
cogl_features_available ()
CoglBool
cogl_features_available (CoglFeatureFlags features);
cogl_features_available has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_has_feature() instead
Checks whether the given COGL features are available. Multiple
features can be checked for by or-ing them together with the '|'
operator. TRUE is only returned if all of the requested features
are available.
cogl_get_proc_address ()
CoglFuncPtr
cogl_get_proc_address (const char *name);
Gets a pointer to a given GL or GL ES extension function. This acts
as a wrapper around glXGetProcAddress() or whatever is the
appropriate function for the current backend.
cogl_get_option_group ()
GOptionGroup *
cogl_get_option_group (void);
cogl_get_option_group has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Not replaced
Retrieves the GOptionGroup used by Cogl to parse the command line options. Clutter uses this to handle the Cogl command line options during its initialization process.
Since: 1.0
cogl_push_matrix ()
void
cogl_push_matrix (void);
cogl_push_matrix has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_push_matrix() instead
Stores the current model-view matrix on the matrix stack. The matrix
can later be restored with cogl_pop_matrix().
cogl_pop_matrix ()
void
cogl_pop_matrix (void);
cogl_pop_matrix has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_pop_matrix() instead
Restores the current model-view matrix from the matrix stack.
cogl_scale ()
void cogl_scale (float x,float y,float z);
cogl_scale has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_pop_matrix() instead
Multiplies the current model-view matrix by one that scales the x, y and z axes by the given values.
cogl_translate ()
void cogl_translate (float x,float y,float z);
cogl_translate has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_translate() instead
Multiplies the current model-view matrix by one that translates the model along all three axes according to the given values.
cogl_rotate ()
void cogl_rotate (float angle,float x,float y,float z);
cogl_rotate has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_rotate() instead
Multiplies the current model-view matrix by one that rotates the
model around the vertex specified by x
, y
and z
. The rotation
follows the right-hand thumb rule so for example rotating by 10
degrees about the vertex (0, 0, 1) causes a small counter-clockwise
rotation.
cogl_transform ()
void
cogl_transform (const CoglMatrix *matrix);
cogl_transform has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_transform() instead
Multiplies the current model-view matrix by the given matrix.
Since: 1.4
cogl_frustum ()
void cogl_frustum (float left,float right,float bottom,float top,float z_near,float z_far);
cogl_frustum has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_frustum() instead
Replaces the current projection matrix with a perspective matrix for a given viewing frustum defined by 4 side clip planes that all cross through the origin and 2 near and far clip planes.
Parameters
left |
X position of the left clipping plane where it intersects the near clipping plane |
|
right |
X position of the right clipping plane where it intersects the near clipping plane |
|
bottom |
Y position of the bottom clipping plane where it intersects the near clipping plane |
|
top |
Y position of the top clipping plane where it intersects the near clipping plane |
|
z_near |
The distance to the near clipping plane (Must be positive) |
|
z_far |
The distance to the far clipping plane (Must be positive) |
Since: 0.8.2
cogl_perspective ()
void cogl_perspective (float fovy,float aspect,float z_near,float z_far);
cogl_perspective has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_perspective() instead
Replaces the current projection matrix with a perspective matrix based on the provided values.
z_far / z_near
ratio since that will reduce the effectiveness of depth testing
since there wont be enough precision to identify the depth of
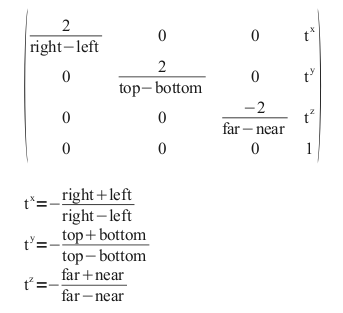
objects near to each other.cogl_ortho ()
void cogl_ortho (float left,float right,float bottom,float top,float near,float far);
cogl_ortho has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_orthographic() instead
Replaces the current projection matrix with an orthographic projection matrix. See Figure 1, “” to see how the matrix is calculated.
glOrtho() even
though they are unnecessarily confusing due to the z near and z far
arguments actually being a "distance" from the origin, where
negative values are behind the viewer, instead of coordinates for
the z clipping planes which would have been consistent with the
left, right bottom and top arguments.Parameters
left |
The coordinate for the left clipping plane |
|
right |
The coordinate for the right clipping plane |
|
bottom |
The coordinate for the bottom clipping plane |
|
top |
The coordinate for the top clipping plane |
|
near |
The distance to the near clipping plane (negative if the plane is behind the viewer) |
|
far |
The distance for the far clipping plane (negative if the plane is behind the viewer) |
Since: 1.0
cogl_get_modelview_matrix ()
void
cogl_get_modelview_matrix (CoglMatrix *matrix);
cogl_get_modelview_matrix has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_get_modelview_matrix()
instead
Stores the current model-view matrix in matrix
.
cogl_set_modelview_matrix ()
void
cogl_set_modelview_matrix (CoglMatrix *matrix);
cogl_set_modelview_matrix has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_set_modelview_matrix()
instead
Loads matrix
as the new model-view matrix.
cogl_get_projection_matrix ()
void
cogl_get_projection_matrix (CoglMatrix *matrix);
cogl_get_projection_matrix has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_get_projection_matrix()
instead
Stores the current projection matrix in matrix
.
cogl_set_projection_matrix ()
void
cogl_set_projection_matrix (CoglMatrix *matrix);
cogl_set_projection_matrix has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_set_projection_matrix()
instead
Loads matrix as the new projection matrix.
cogl_set_viewport ()
void cogl_set_viewport (int x,int y,int width,int height);
cogl_set_viewport has been deprecated since version 1.8 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_set_viewport() instead
Replaces the current viewport with the given values.
Parameters
x |
X offset of the viewport |
|
y |
Y offset of the viewport |
|
width |
Width of the viewport |
|
height |
Height of the viewport |
Since: 1.2
cogl_get_viewport ()
void
cogl_get_viewport (float v[4]);
cogl_get_viewport has been deprecated since version 1.10 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_get_viewport4fv()
instead
Stores the current viewport in v
. v
[0] and v
[1] get the x and y
position of the viewport and v
[2] and v
[3] get the width and
height.
cogl_clear ()
void cogl_clear (const CoglColor *color,unsigned long buffers);
cogl_clear has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_clear() api instead
Clears all the auxiliary buffers identified in the buffers
mask, and if
that includes the color buffer then the specified color
is used.
Parameters
color |
Background color to clear to |
|
buffers |
A mask of CoglBufferBit's identifying which auxiliary buffers to clear |
cogl_set_backface_culling_enabled ()
void
cogl_set_backface_culling_enabled (CoglBool setting);
cogl_set_backface_culling_enabled has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_pipeline_set_cull_face_mode() instead
Sets whether textures positioned so that their backface is showing should be hidden. This can be used to efficiently draw two-sided textures or fully closed cubes without enabling depth testing. This only affects calls to the cogl_rectangle* family of functions and cogl_vertex_buffer_draw*. Backface culling is disabled by default.
cogl_get_backface_culling_enabled ()
CoglBool
cogl_get_backface_culling_enabled (void);
cogl_get_backface_culling_enabled has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_pipeline_get_cull_face_mode() instead
Queries if backface culling has been enabled via
cogl_set_backface_culling_enabled()
cogl_set_fog ()
void cogl_set_fog (const CoglColor *fog_color,CoglFogMode mode,float density,float z_near,float z_far);
cogl_set_fog has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use CoglSnippet shader api for fog
Enables fogging. Fogging causes vertices that are further away from the eye
to be rendered with a different color. The color is determined according to
the chosen fog mode; at it's simplest the color is linearly interpolated so
that vertices at z_near
are drawn fully with their original color and
vertices at z_far
are drawn fully with fog_color
. Fogging will remain
enabled until you call cogl_disable_fog().
cogl_set_source_color() will premultiply colors, so unless you
explicitly load your textures requesting an unmultiplied internal format
and use cogl_material_set_color() you can only use fogging with fully
opaque primitives. This might improve in the future when we can depend
on fragment shaders.Parameters
fog_color |
The color of the fog |
|
mode |
A CoglFogMode that determines the equation used to calculate the fogging blend factor. |
|
density |
Used by |
|
z_near |
Position along Z axis where no fogging should be applied |
|
z_far |
Position along Z axis where full fogging should be applied |
cogl_disable_fog ()
void
cogl_disable_fog (void);
cogl_disable_fog has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use CoglSnippet shader api for fog
This function disables fogging, so primitives drawn afterwards will not be blended with any previously set fog color.
cogl_set_source ()
void
cogl_set_source (void *material);
cogl_set_source has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
This function changes the material at the top of the source stack.
The material at the top of this stack defines the GPU state used to
process subsequent primitives, such as rectangles drawn with
cogl_rectangle() or vertices drawn using cogl_vertex_buffer_draw().
Since: 1.0
cogl_set_source_color ()
void
cogl_set_source_color (const CoglColor *color);
cogl_set_source_color has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
This is a convenience function for creating a solid fill source material from the given color. This color will be used for any subsequent drawing operation.
The color will be premultiplied by Cogl, so the color should be non-premultiplied. For example: use (1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5) for semi-transparent red.
See also cogl_set_source_color4ub() and cogl_set_source_color4f()
if you already have the color components.
Since: 1.0
cogl_set_source_color4ub ()
void cogl_set_source_color4ub (uint8_t red,uint8_t green,uint8_t blue,uint8_t alpha);
cogl_set_source_color4ub has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
This is a convenience function for creating a solid fill source material from the given color using unsigned bytes for each component. This color will be used for any subsequent drawing operation.
The value for each component is an unsigned byte in the range between 0 and 255.
Parameters
red |
value of the red channel, between 0 and 255 |
|
green |
value of the green channel, between 0 and 255 |
|
blue |
value of the blue channel, between 0 and 255 |
|
alpha |
value of the alpha channel, between 0 and 255 |
Since: 1.0
cogl_set_source_color4f ()
void cogl_set_source_color4f (float red,float green,float blue,float alpha);
cogl_set_source_color4f has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
This is a convenience function for creating a solid fill source material from the given color using normalized values for each component. This color will be used for any subsequent drawing operation.
The value for each component is a fixed point number in the range
between 0 and 1.0. If the values passed in are outside that
range, they will be clamped.
Parameters
red |
value of the red channel, between 0 and |
|
green |
value of the green channel, between 0 and |
|
blue |
value of the blue channel, between 0 and |
|
alpha |
value of the alpha channel, between 0 and |
Since: 1.0
cogl_set_source_texture ()
void
cogl_set_source_texture (CoglTexture *texture);
cogl_set_source_texture has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
This is a convenience function for creating a material with the first
layer set to texture
and setting that material as the source with
cogl_set_source.
Note: There is no interaction between calls to cogl_set_source_color and cogl_set_source_texture. If you need to blend a texture with a color then you can create a simple material like this:
material = cogl_material_new (); cogl_material_set_color4ub (material, 0xff, 0x00, 0x00, 0x80); cogl_material_set_layer (material, 0, tex_handle); cogl_set_source (material);
Since: 1.0
cogl_get_source ()
void *
cogl_get_source (void);
cogl_get_source has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
Returns the current source material as previously set using
cogl_set_source().
Since: 1.6
cogl_push_source ()
void
cogl_push_source (void *material);
cogl_push_source has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
Pushes the given material
to the top of the source stack. The
material at the top of this stack defines the GPU state used to
process later primitives as defined by cogl_set_source().
Since: 1.6
cogl_pop_source ()
void
cogl_pop_source (void);
cogl_pop_source has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Latest drawing apis all take an explicit CoglPipeline argument so this stack of CoglMaterials shouldn't be used.
Removes the material at the top of the source stack. The material
at the top of this stack defines the GPU state used to process
later primitives as defined by cogl_set_source().
Since: 1.6
cogl_read_pixels ()
void cogl_read_pixels (int x,int y,int width,int height,CoglReadPixelsFlags source,CoglPixelFormat format,uint8_t *pixels);
cogl_read_pixels has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use cogl_framebuffer_read_pixels() instead
This reads a rectangle of pixels from the current framebuffer where position (0, 0) is the top left. The pixel at (x, y) is the first read, and the data is returned with a rowstride of (width * 4).
Currently Cogl assumes that the framebuffer is in a premultiplied
format so if format
is non-premultiplied it will convert it. To
read the pixel values without any conversion you should either
specify a format that doesn't use an alpha channel or use one of
the formats ending in PRE.
Parameters
x |
The window x position to start reading from |
|
y |
The window y position to start reading from |
|
width |
The width of the rectangle you want to read |
|
height |
The height of the rectangle you want to read |
|
source |
Identifies which auxillary buffer you want to read (only COGL_READ_PIXELS_COLOR_BUFFER supported currently) |
|
format |
The pixel format you want the result in (only COGL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGBA_8888 supported currently) |
|
pixels |
The location to write the pixel data. |
cogl_flush ()
void
cogl_flush (void);
This function should only need to be called in exceptional circumstances.
As an optimization Cogl drawing functions may batch up primitives internally, so if you are trying to use raw GL outside of Cogl you stand a better chance of being successful if you ask Cogl to flush any batched geometry before making your state changes.
It only ensure that the underlying driver is issued all the commands necessary to draw the batched primitives. It provides no guarantees about when the driver will complete the rendering.
This provides no guarantees about the GL state upon returning and to avoid confusing Cogl you should aim to restore any changes you make before resuming use of Cogl.
If you are making state changes with the intention of affecting Cogl drawing primitives you are 100% on your own since you stand a good chance of conflicting with Cogl internals. For example clutter-gst which currently uses direct GL calls to bind ARBfp programs will very likely break when Cogl starts to use ARBfb programs itself for the material API.
Since: 1.0
cogl_begin_gl ()
void
cogl_begin_gl (void);
cogl_begin_gl has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use the CoglGLES2Context api instead
We do not advise nor reliably support the interleaving of raw GL drawing and
Cogl drawing functions, but if you insist, cogl_begin_gl() and cogl_end_gl()
provide a simple mechanism that may at least give you a fighting chance of
succeeding.
Note: this doesn't help you modify the behaviour of Cogl drawing functions through the modification of GL state; that will never be reliably supported, but if you are trying to do something like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{ - setup some OpenGL state. - draw using OpenGL (e.g. glDrawArrays() ) - reset modified OpenGL state. - continue using Cogl to draw } |
You should surround blocks of drawing using raw GL with cogl_begin_gl()
and cogl_end_gl():
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
{ cogl_begin_gl (); - setup some OpenGL state. - draw using OpenGL (e.g. glDrawArrays() ) - reset modified OpenGL state. cogl_end_gl (); - continue using Cogl to draw } |
Don't ever try and do:
1 2 3 4 5 |
{ - setup some OpenGL state. - use Cogl to draw - reset modified OpenGL state. } |
When the internals of Cogl evolves, this is very liable to break.
This function will flush all batched primitives, and subsequently flush all internal Cogl state to OpenGL as if it were going to draw something itself.
The result is that the OpenGL modelview matrix will be setup; the state corresponding to the current source material will be set up and other world state such as backface culling, depth and fogging enabledness will be sent to OpenGL.
cogl_begin_gl(). E.g. by calling
cogl_set_source_color4ub().cogl_begin_gl() if you don't do this then the
result of further Cogl calls is undefined.Again we would like to stress, we do not advise the use of this API and if possible we would prefer to improve Cogl than have developers require raw OpenGL.
Since: 1.0
cogl_end_gl ()
void
cogl_end_gl (void);
cogl_end_gl has been deprecated since version 1.16 and should not be used in newly-written code.
Use the CoglGLES2Context api instead
This is the counterpart to cogl_begin_gl() used to delimit blocks of drawing
code using raw OpenGL. Please refer to cogl_begin_gl() for full details.
Since: 1.0
Types and Values
CoglObject
typedef struct _CoglObject CoglObject;
Ref Func: cogl_object_ref Unref Func: cogl_object_unref Set Value Func: cogl_object_value_set_object Get Value Func: cogl_object_value_get_object
CoglUserDataKey
typedef struct {
int unused;
} CoglUserDataKey;
A CoglUserDataKey is used to declare a key for attaching data to a CoglObject using cogl_object_set_user_data. The typedef only exists as a formality to make code self documenting since only the unique address of a CoglUserDataKey is used.
Typically you would declare a static CoglUserDataKey and set private data on an object something like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
static CoglUserDataKey path_private_key; static void destroy_path_private_cb (void *data) { g_free (data); } static void my_path_set_data (CoglPath *path, void *data) { cogl_object_set_user_data (COGL_OBJECT (path), &private_key, data, destroy_path_private_cb); } |
Since: 1.4
COGL_INVALID_HANDLE
#define COGL_INVALID_HANDLE NULL
A COGL handle that is not valid, used for unitialized handles as well as error conditions.
CoglHandle
typedef void * CoglHandle;
Type used for storing references to cogl objects, the CoglHandle is a fully opaque type without any public data members.
enum CoglPixelFormat
Pixel formats used by Cogl. For the formats with a byte per
component, the order of the components specify the order in
increasing memory addresses. So for example
COGL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_888 would have the red component in the
lowest address, green in the next address and blue after that
regardless of the endianness of the system.
For the formats with non byte aligned components the component
order specifies the order within a 16-bit or 32-bit number from
most significant bit to least significant. So for
COGL_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565, the red component would be in bits
11-15, the green component would be in 6-11 and the blue component
would be in 1-5. Therefore the order in memory depends on the
endianness of the system.
When uploading a texture COGL_PIXEL_FORMAT_ANY can be used as the
internal format. Cogl will try to pick the best format to use
internally and convert the texture data if necessary.
Members
|
Any format |
||
|
8 bits alpha mask |
||
|
RGB, 16 bits |
||
|
RGBA, 16 bits |
||
|
RGBA, 16 bits |
||
|
Not currently supported |
||
|
Single luminance component |
||
|
RG, 16 bits. Note that red-green textures
are only available if |
||
|
RGB, 24 bits |
||
|
BGR, 24 bits |
||
|
RGBA, 32 bits |
||
|
BGRA, 32 bits |
||
|
ARGB, 32 bits |
||
|
ABGR, 32 bits |
||
|
RGBA, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
BGRA, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
ARGB, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
ABGR, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
Premultiplied RGBA, 32 bits |
||
|
Premultiplied BGRA, 32 bits |
||
|
Premultiplied ARGB, 32 bits |
||
|
Premultiplied ABGR, 32 bits |
||
|
Premultiplied RGBA, 16 bits |
||
|
Premultiplied RGBA, 16 bits |
||
|
Premultiplied RGBA, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
Premultiplied BGRA, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
Premultiplied ARGB, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
|
Premultiplied ABGR, 32 bits, 10 bpc |
||
Since: 0.8
enum CoglAttributeType
Data types for the components of a vertex attribute.
Members
|
Data is the same size of a byte |
||
|
Data is the same size of an unsigned byte |
||
|
Data is the same size of a short integer |
||
|
Data is the same size of an unsigned short integer |
||
|
Data is the same size of a float |
Since: 1.0
enum CoglFeatureFlags
Flags for the supported features.
Members
|
ARB_texture_rectangle support |
||
|
Non power of two textures are supported
by the hardware. This is a equivalent to the
|
||
|
ycbcr conversion support |
||
|
glReadPixels() support |
||
|
GLSL support |
||
|
FBO support |
||
|
Multisample support on FBOs |
||
|
Blit support on FBOs |
||
|
At least 4 clip planes available |
||
|
Stencil buffer support |
||
|
VBO support |
||
|
PBO support |
||
|
Set if
|
||
|
cogl_material_set_depth_range() support |
||
|
The hardware supports non power
of two textures, but you also need to check the
|
||
|
Mipmapping is supported in conjuntion with non power of two textures. |
||
|
Repeat modes other than
|
||
|
Whether
|
||
|
3D texture support |
||
|
ARBFP support |
||
|
Whether |
||
|
Whether |
||
|
Whether CoglFramebuffer support rendering the depth buffer to a texture. |
Since: 0.8
enum CoglFogMode
The fog mode determines the equation used to calculate the fogging blend
factor while fogging is enabled. The simplest COGL_FOG_MODE_LINEAR mode
determines f as:
1 |
f = end - eye_distance / end - start |
Where eye_distance is the distance of the current fragment in eye coordinates from the origin.
Members
|
Calculates the fog blend factor as:
|
||||
|
Calculates the fog blend factor as:
|
||||
|
Calculates the fog blend factor as:
|
Since: 1.0